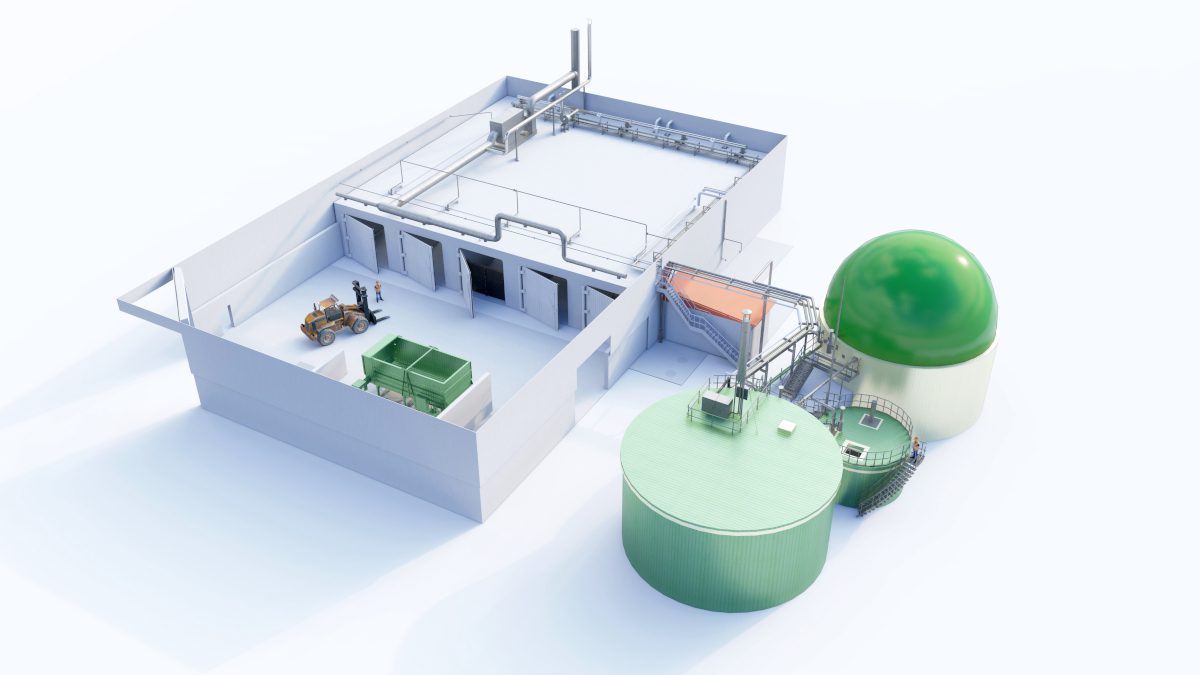
At a meeting on 17 January, the Greater Manchester Combined Authority (GMCA) Waste and Recycling Committee approved an option to commission the building in the North West of two dry1 anaerobic digestion (AD) plants – the very first plants ever built in England – as part of its Biowaste Management Strategy. The Strategy will now be submitted to the GMCA for full approval.
“This is a fantastic breakthrough for our industry”, commented Charlotte Morton OBE, Chief Executive of the Anaerobic Digestion and Bioresources Association (ADBA). “Dry anaerobic digestion facilitates the treatment of garden waste in addition to food waste, and transforms these wastes into green gas, biofertilisers and bioCO2 for use in the energy, agriculture and food and drink sectors.”
“According to ADBA’s calculations, 1million tonnes of garden waste could generate approximately 1.0 TWh of green energy – and there were 6.8 million tonnes of garden waste available in 2021. Garden waste is England’s untapped energy source; by treating those 6.8 million tonnes of waste through dry AD, an additional 6.8 TWh of biogas could be used to heat nearly 567,000 homes, generate electricity, and power our way to net zero.”
“The plan by Greater Manchester Combined Authority to potentially commission dry AD plants to recycle their biowaste will give a further boost to the UK’s climate change mitigation efforts by enabling both the effective management of organic wastes and the decarbonisation of carbon-intensive industries in the UK through the AD treatment of solid organic wastes.”
ADBA said dry AD is a well-established technology and is being used in Europe and other parts of the world, and that interest in the UK is growing.
Notes
[1] The difference between “dry” and “wet” AD lies in the composition of the feedstock – with water added to the waste mixture if the solid content is too high for the “wet” AD treatment process – currently the only one available in England.








