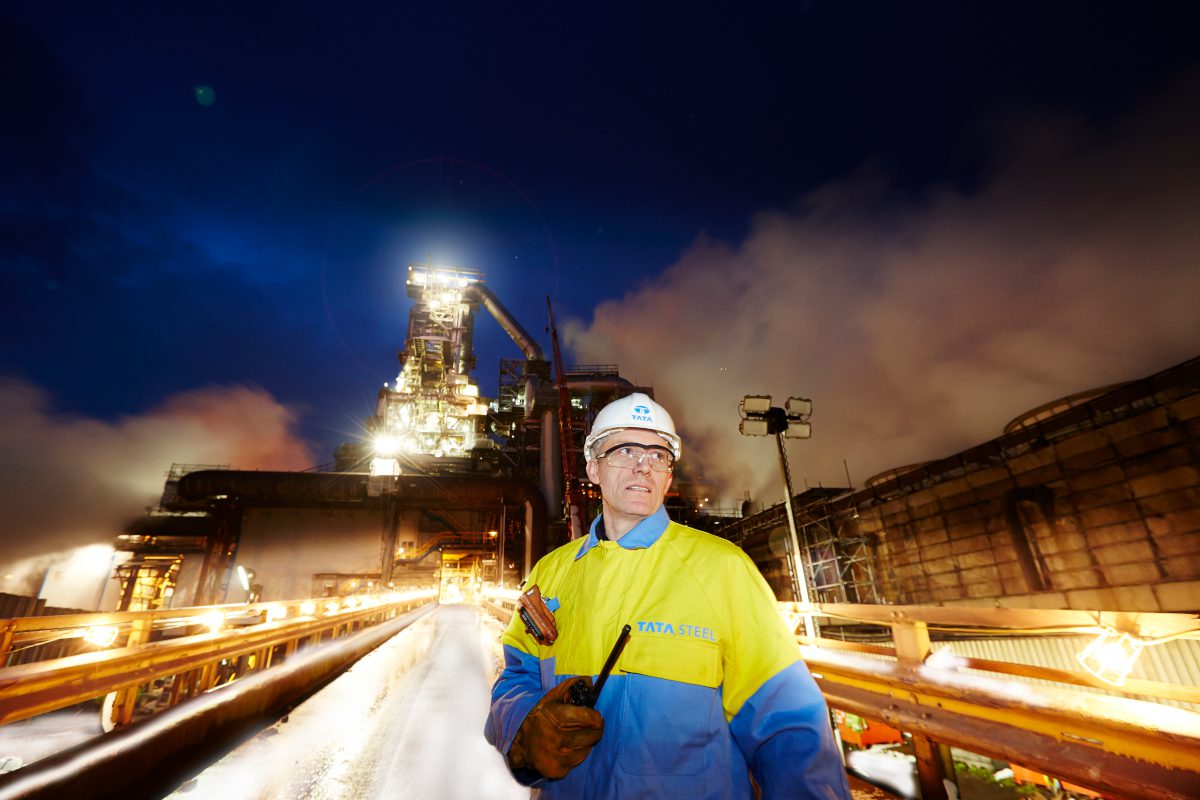
A trial is studying the use of bacteria to convert emissions from Tata Steel’s blast furnaces into products which could be used by other industries to make products such as food packaging and animal feed.
The pilot project, led by the University of South Wales, has been set up at the two huge Port Talbot iron-making furnaces, and it has already shown promising results, says the group.
Dr Rhiannon Chalmers-Brown from the university, said: “As the world is coming to terms with the challenges of net-zero CO2 steelmaking, there are lots of options to consider. Not only in terms of different steelmaking technologies, but also around any opportunities to capture and use the carbon-based process gases.
“The process we are testing here bubbles off-gases from the blast furnaces through sewage sludge, which contains a certain type of bacteria which is able to consume both carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide.”
She added: “We’re currently getting quite high levels of carbon utilisation which we think we can increase up to about 98%.
“The waste products from those bacteria include acetic acid and volatile fatty acids which can be used for a huge range of commercially viable end-uses such as paints, bioplastic-polymers or even animal feeds.”
The project is the latest collaboration between Tata Steel and the university exploring how waste gasses from the steelmaking processes at Port Talbot can be harnessed and used to support other industries while reducing the amount of CO2 released.
Dr Chalmers-Brown added: “While this pilot is looking at gases from blast furnaces, pretty much every iron and steelmaking technology emits some carbon-based gases, so this technology has potential to reduce those emissions whichever technology route is eventually chosen.
“There’s still quite a lot of work to do with the pilot reactor, collecting data and to understand what we can about the biological reactions.”
Gareth Lloyd, Process Engineering Manager from Tata Steel and industry sponsor, added: “This is a great project, which could be a real game-changer and is yet another example of the benefits of working closely with some of our top universities.”
Tata Steel in the UK has delcared an ambition to produce net-zero steel by 2050 at the latest and to have eliminated 30% of CO2 emissions by 2030. The vast majority of that work will need to happen in South Wales, the location of the company’s largest operational site.